Plastic Molding Manufacturers
Plastic processes differ greatly in both the way they form plastic products and in the shape and structural integrity of the products they manufacture. Blow molding, for example, is nearly the sole method by which plastic bottles for beverages, household cleaners and cosmetic products are made, as well as a range of low-cost toys and parts with low to medium performance.
Plastic processing methods vary significantly in how they shape and form products, impacting the final structure and integrity of the items produced. Take blow molding, for instance. This technique is almost exclusively used to create plastic bottles for beverages, household cleaners, and cosmetics. Additionally, it is used to produce a variety of low-cost toys and components with low to medium performance.
Plastic Molding Manufacturers
Plastic molding is the process of shaping liquid or pliable plastic into customized forms by using a mold, die, or press. It is the foundation of modern manufacturing, creating everything from automotive dashboards and bottle caps to medical components and packaging. Because of its versatility, plastic molding has become the preferred alternative to wood, glass, or metal—capable of delivering strength, durability, and cost efficiency at scale. Today, companies like Flambeau, Flexcraft, Amtech, PolyOne, Lincoln Industries, and Fibertech demonstrate how advanced molding methods can be applied across industries ranging from consumer goods to aerospace.
When customers search for plastic injection molding near me or a plastic factory near me, they are usually looking for local suppliers who can deliver high-volume runs of quality parts with fast turnaround. Whether it’s MRPC and Nolato producing medical devices, Freudenberg Medical manufacturing precision seals, or Pexco and Makray fabricating industrial profiles, the molding process is what enables these manufacturers to provide custom solutions at scale.
Plastic Molding Types
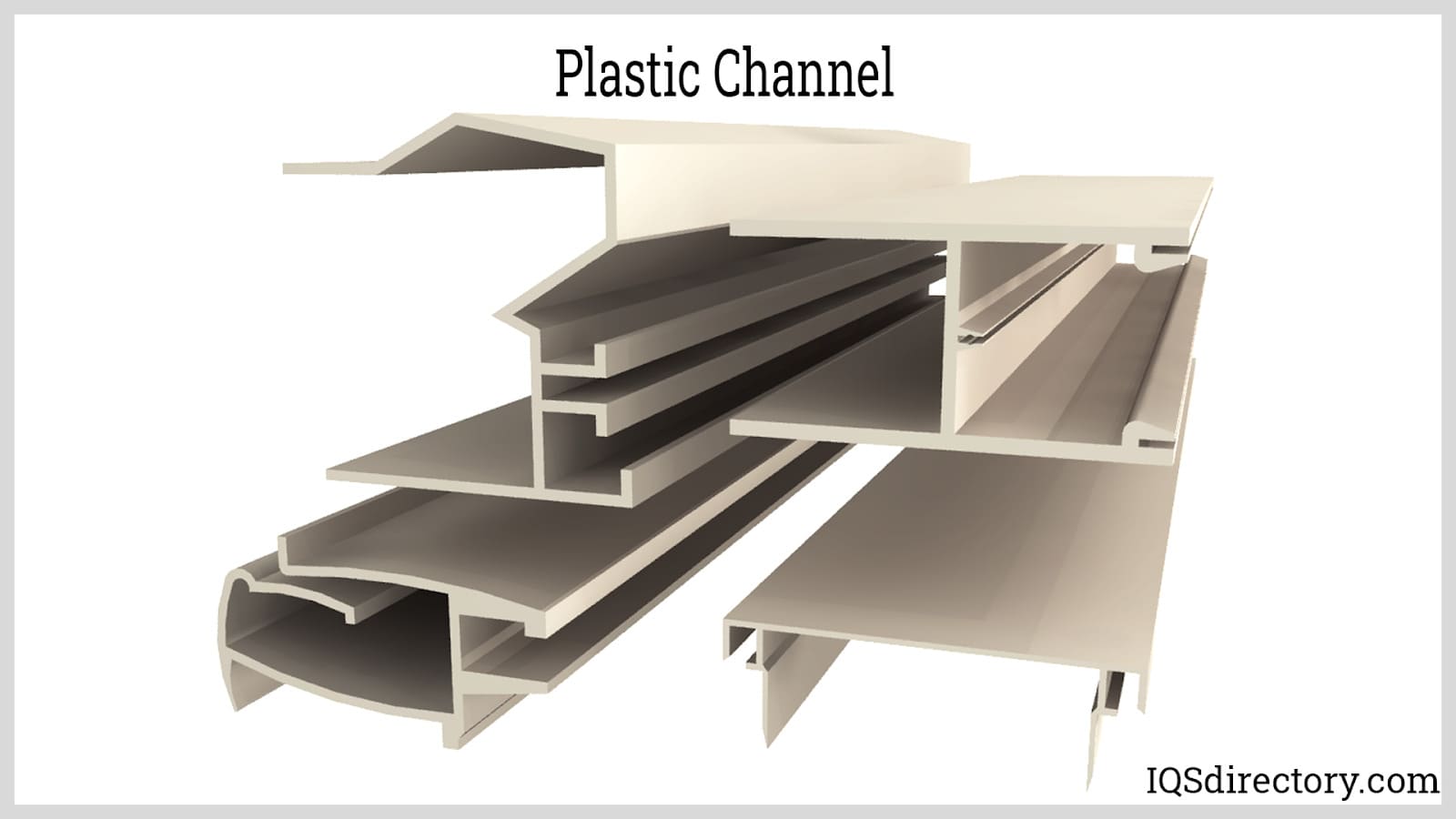
Extrusion Molding
In extrusion molding, melted plastic is pushed through a custom die to create long, continuous shapes—similar to how dough passes through a press to make uniform cookies. The result is a product with the same profile along its length, such as PVC pipes, weatherstrips, or plastic straws. This process is relatively low-cost, highly productive, and ideal for large-scale manufacturing, though it is limited to parts with uniform cross-sections.
Plastic extrusion manufacturing services have evolved to include co-extrusion techniques, where multiple plastic materials are simultaneously extruded to create multi-layer products with enhanced properties. Custom plastic extrusion companies now offer specialized solutions for window profiles, door frames, medical tubing, and automotive weatherstripping. The continuous extrusion process allows manufacturers to produce miles of consistent plastic profiles daily, making it ideal for construction materials, electrical conduits, and flexible plastic tubing applications. Advanced extrusion molding equipment can handle complex hollow profiles and multi-durometer products, expanding the range of applications from simple plastic strips to sophisticated architectural components and industrial gaskets.
Compression Molding
Compression molding involves placing heated plastic into a mold, compressing it under pressure, and cooling it to form a durable part. Because this method produces strong components with excellent dimensional stability, it is often used to replace heavier metal parts. Industries rely on this process for automotive panels, appliance housings, and high-strength replacement components. The cost per part decreases significantly with mass production, making it a reliable choice for manufacturers.
Thermoset compression molding services excel at producing high-strength composite parts using materials like BMC (bulk molding compound), SMC (sheet molding compound), and phenolic resins. Custom compression molding manufacturers specialize in automotive under-hood components, electrical insulators, and heavy-duty industrial parts that require superior heat resistance and dimensional stability. The compression molding process is particularly valuable for rubber molding applications, creating seals, gaskets, O-rings, and vibration dampeners. Many compression molding companies near me offer rapid prototyping services and low-volume production runs, making this process accessible for startups and established manufacturers seeking cost-effective alternatives to injection molding for specific applications.
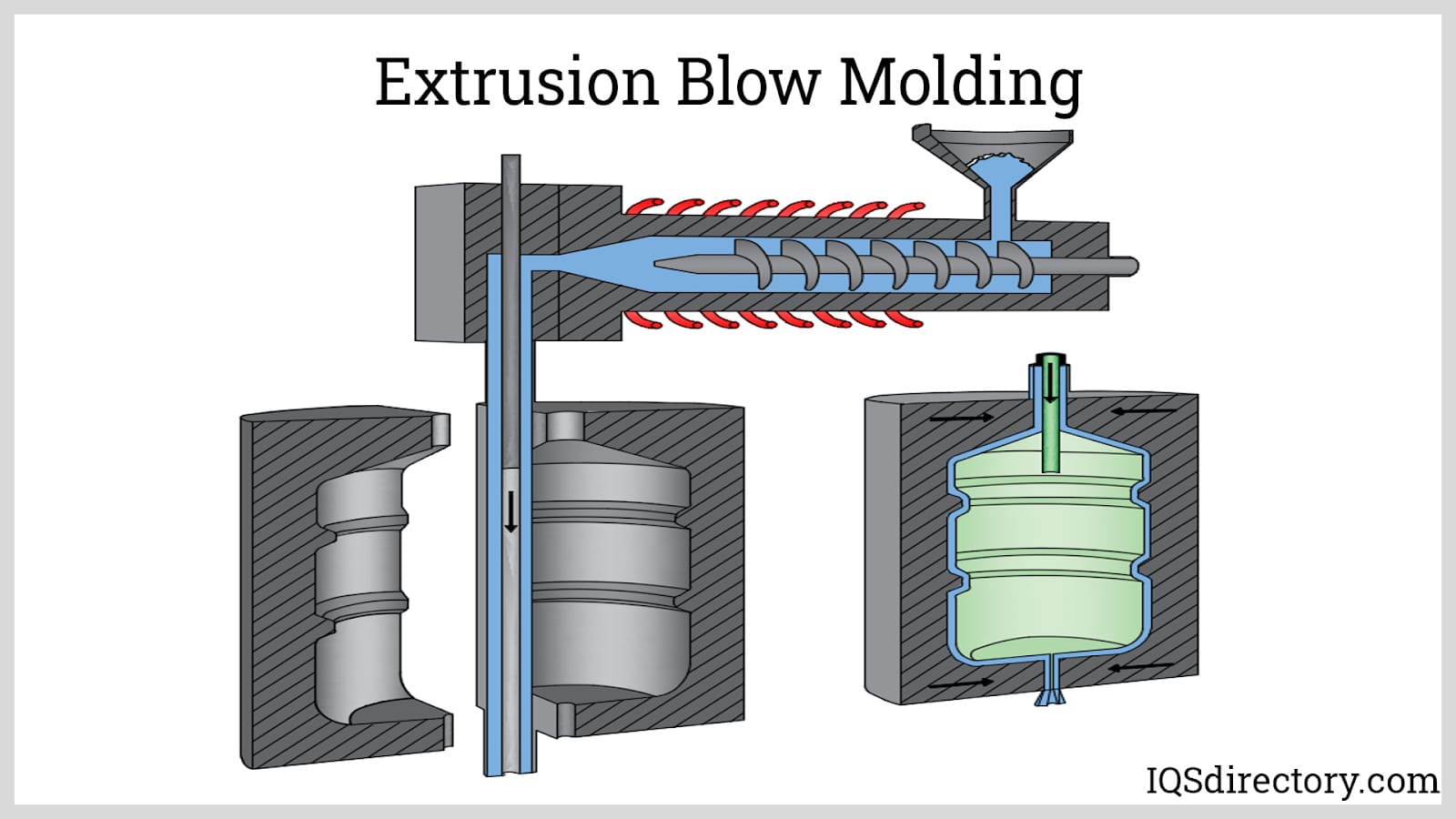
Blow Molding
Blow molding creates hollow, thin-walled parts with uniform thickness, much like glass blowing. Heated plastic is inflated inside a mold until it takes shape, then cooled to form sturdy, lightweight products. This technique is most common in the packaging industry, producing plastic bottles, drums, and fuel tanks. For companies needing hundreds of thousands of identical units, blow molding is one of the most economical options.
Injection blow molding services combine the precision of injection molding with the hollow-forming capabilities of blow molding, making it ideal for small medical containers, pharmaceutical bottles, and precision cosmetic packaging. Extrusion blow molding manufacturers focus on larger containers like milk jugs, detergent bottles, automotive fluid reservoirs, and industrial chemical containers. Stretch blow molding companies specialize in producing PET bottles for beverages, offering superior clarity and barrier properties. Custom blow molding services now include multi-layer blow molding for enhanced product protection, co-injection blow molding for cost reduction, and 3D blow molding for complex geometric shapes. Many blow molding manufacturers near me provide complete packaging solutions, including custom labeling, printing, and secondary operations like handle attachment and thread finishing.
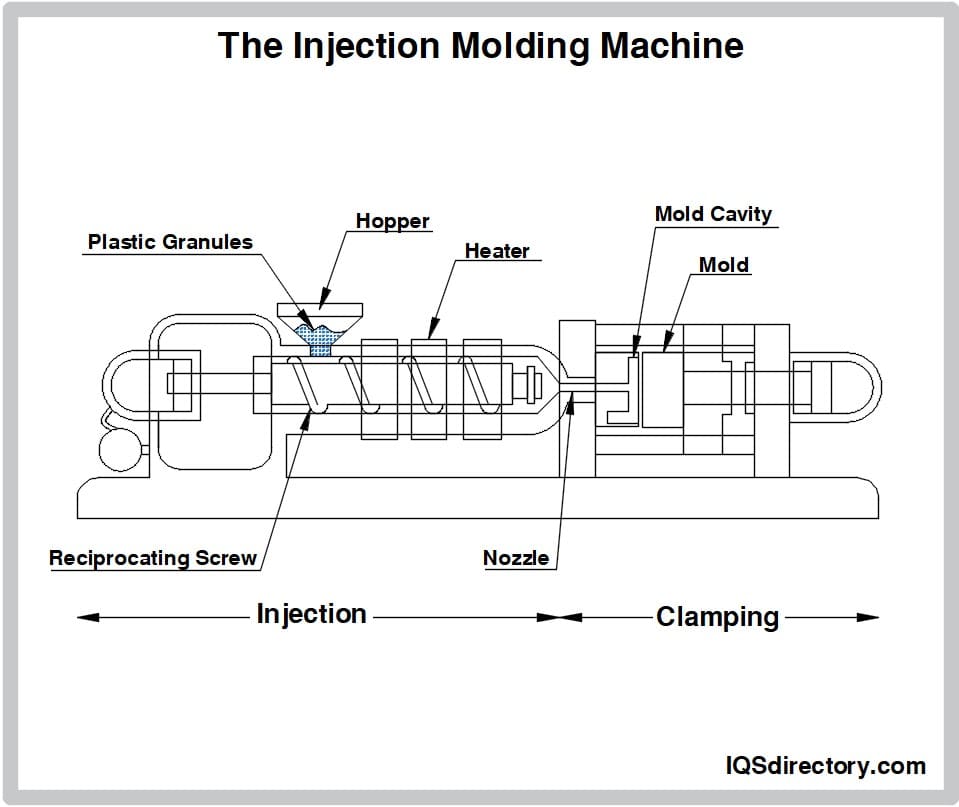
Injection Molding
Injection molding is one of the most widely recognized and advanced forms of plastic manufacturing. In this process, molten resin is injected into a steel or aluminum mold under high pressure, cooled, and ejected as a solid part. It is used to produce everything from car parts and medical devices to surgical components and consumer electronics. While molds can be expensive and tooling may take weeks to complete, the precision and efficiency of injection molding make it the gold standard for high-volume production. Companies like Flextech and MRPC have built their reputations around injection molding capabilities.
Precision injection molding services have expanded to include micro-molding for electronic components, insert molding for metal-plastic assemblies, and overmolding for ergonomic grips and soft-touch surfaces. Multi-shot injection molding manufacturers create complex parts with multiple colors or materials in a single cycle, eliminating assembly steps and reducing costs. Liquid silicone rubber (LSR) injection molding companies specialize in medical-grade seals, baby products, and automotive gaskets that require biocompatibility and high-temperature resistance. Custom injection molding services now encompass rapid prototyping with 3D-printed molds, low-volume production with aluminum tooling, and high-cavitation molds for maximum efficiency. Many plastic injection molding companies near me offer complete design-to-delivery solutions, including mold design optimization, material selection guidance, and automated assembly integration.
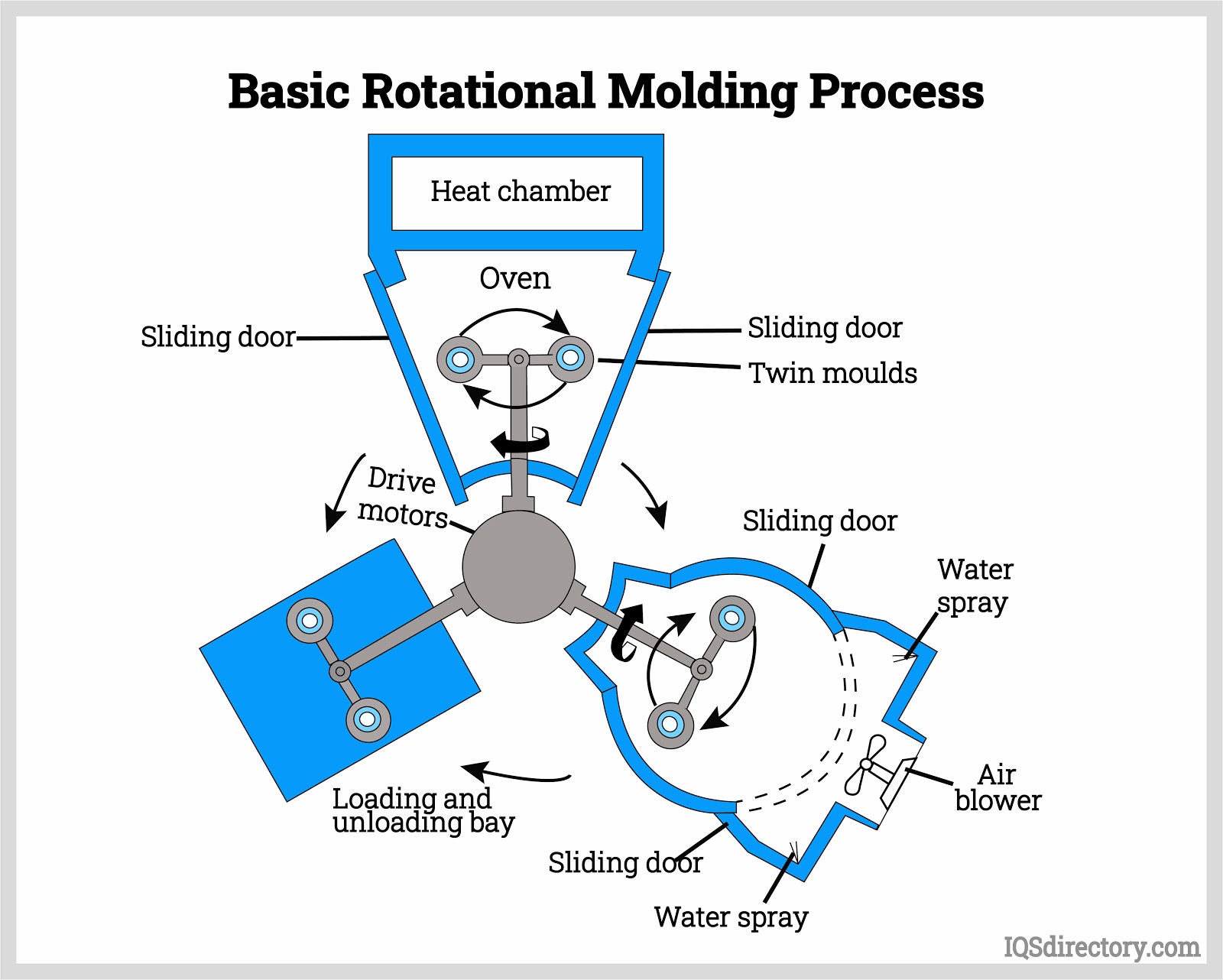
Rotational Molding
Also known as rotomolding, this process involves coating the interior of a spinning mold with liquid resin, forming hollow items with consistent wall thickness. Because very little material is wasted, it is both cost-effective and environmentally friendly. Rotomolding is ideal for larger items such as kayaks, storage tanks, road cones, or pet shelters. Manufacturers like Fibertech and Lincoln Industries employ this method for its design flexibility and ability to incorporate features like logos, textures, or inserts directly into the finished product.
Custom rotational molding services excel at producing large hollow parts that would be cost-prohibitive with other molding methods. Rotomolding manufacturers specialize in creating playground equipment, agricultural tanks, marine buoys, and outdoor furniture with complex geometries and integrated features. The rotational molding process allows for uniform wall thickness distribution, making it ideal for products requiring consistent strength throughout. Many rotomolding companies near me offer foam-filled rotational molding for enhanced insulation properties, multi-wall rotational molding for structural strength, and color-matched rotational molding for aesthetic applications. Advanced rotomolding techniques include rock-and-roll molding for elongated products, shuttle molding for higher production rates, and clamshell molding for complex part geometries with multiple access points.
Materials in Plastic Molding
The choice of material impacts the strength, flexibility, and longevity of the molded part. Thermoplastics, such as polypropylene and polyethylene, soften with heat and can be remolded multiple times, though they may be brittle in cold environments. Thermosets, like melamine resin, harden permanently after molding and are valued in high-heat or cold-exposure applications. Elastomers, including rubber compounds, retain elasticity and are frequently used for comfort-driven products like seals, grips, and handles.
Engineering grade plastic molding materials have revolutionized industrial applications, with high-performance polymers like PEEK, PEI, and PPS offering exceptional chemical resistance, high-temperature stability, and mechanical strength. Bio-compatible plastic molding materials such as medical-grade PEEK, USP Class VI silicones, and FDA-approved polyethylenes enable critical healthcare applications from surgical instruments to drug delivery devices. Recycled plastic molding materials are gaining popularity as manufacturers seek sustainable alternatives without compromising performance, with post-consumer recycled resins now available for automotive, packaging, and consumer goods applications. Specialty plastic molding compounds include glass-filled nylons for structural components, carbon fiber reinforced plastics for aerospace applications, and flame-retardant materials for electrical housings and automotive interior parts.
Advantages of Plastic Molding
Plastic molding offers fast turnaround, reduced labor costs, and the ability to create intricate, high-tolerance designs with minimal waste. Unlike machining wood or metal, which can leave behind significant scrap, most molding waste can be recycled back into the process. With the expertise of established manufacturers—from Nolato and Freudenberg Medical in healthcare to Makray and Pexco in industrial solutions—plastic molding continues to be an essential, sustainable, and cost-effective production method.
Beyond efficiency and sustainability, plastic molding has additional advantages that drive its widespread use across industries. One of the biggest strengths of the process is design freedom. Plastic can be molded into complex geometries that are nearly impossible to achieve with traditional materials such as wood or metal. Engineers and designers can take advantage of this flexibility to integrate multiple functions into a single part, reducing assembly time and cost. A simple example is the way automotive dashboards are molded with built-in mounting points, vents, and supports, eliminating the need for separate components. This versatility extends to industries like medical manufacturing, where companies such as Freudenberg Medical and MRPC produce highly specialized components with tight tolerances for surgical instruments and drug delivery systems. Another important benefit is scalability. Once tooling is created, processes like plastic injection molding and blow molding can run continuously, producing millions of identical parts at a low per-unit cost. This makes plastic molding not only the best option for mass-market consumer products like packaging and toys, but also for critical industries where repeatability is essential, including aerospace and automotive. Manufacturers like Flambeau, Flexcraft, and Amtech rely on these efficiencies to serve diverse markets with speed and consistency. Even smaller operations looking for a plastic factory near me can tap into the scalability of molding to compete with larger enterprises. Material selection is another advantage. With options ranging from lightweight thermoplastics to high-performance thermosets and elastomers, molded parts can be engineered for durability, flexibility, impact resistance, or elasticity depending on the application. Companies such as PolyOne and Pexco have built their businesses around developing and applying specialized polymers to meet the needs of industries as varied as healthcare, consumer electronics, and industrial equipment. This ability to customize performance characteristics ensures that plastic molding remains a solution-oriented technology, capable of adapting to changing market demands. Cost-effectiveness also sets plastic molding apart. While the initial tooling for processes like injection molding can be expensive, the long-term savings from automation, material efficiency, and high output outweigh the investment. Manufacturers like Lincoln Industries and Fibertech demonstrate how even lower-volume applications benefit from the affordability of rotational molding or thermoforming. When combined with minimal waste and recyclability, the overall value of plastic molding becomes clear: it offers manufacturers a way to meet performance requirements while keeping production budgets in check. Finally, accessibility is a defining factor. From global leaders like Nolato and Makray to regional suppliers advertising plastic injection molding near me, the widespread availability of molding expertise ensures businesses at every scale can access the technology. Whether the project calls for thousands of lightweight bottles, durable automotive components, or complex medical devices, plastic molding provides an efficient, adaptable, and environmentally responsible solution. This combination of design flexibility, material variety, scalability, and affordability explains why it continues to dominate modern manufacturing and why companies across the globe, from Flextech to Freudenberg Medical, continue to innovate within this field.
What are the main types of plastic molding processes?
The main types of plastic molding processes include injection molding, blow molding, extrusion molding, compression molding, and rotational molding (rotomolding). Each method has unique advantages and is suited to specific product requirements and applications.
Which products are commonly made with blow molding?
Blow molding is widely used to produce plastic bottles for beverages, household cleaners, and cosmetics. It is also used for making drums, fuel tanks, low-cost toys, and various hollow plastic components.
What is the advantage of injection molding over other plastic processing methods?
Injection molding provides high precision, efficiency, and the ability to produce complex, high-tolerance designs with minimal waste. It is ideal for high-volume manufacturing and is capable of producing millions of identical parts at a low per-unit cost.
How is extrusion molding different from other molding methods?
Extrusion molding involves pushing melted plastic through a custom die to form continuous shapes with a uniform profile, such as pipes, straws, and weatherstrips. It is best suited for producing long, straight products and allows for large-scale, cost-effective manufacturing of profiles with consistent cross-sections.
What materials are used in plastic molding, and how do they affect the final product?
Materials used in plastic molding include thermoplastics (such as polypropylene and polyethylene), thermosets (like melamine resin), and elastomers (rubber compounds). The choice of material impacts strength, flexibility, heat resistance, and suitability for specific applications, ranging from automotive parts to medical devices.
What are the advantages of plastic molding compared to traditional manufacturing methods?
Plastic molding offers fast turnaround, reduced labor costs, design flexibility, scalability, minimal waste (with most scrap being recyclable), and the ability to produce highly complex parts not achievable with wood or metal. It is also cost-effective for both small and large-scale manufacturing.
What is rotational molding and what products are suited for this process?
Rotational molding, or rotomolding, is a process where resin coats the inside of a rotating mold to form hollow parts with uniform wall thickness. It is ideal for large items such as kayaks, storage tanks, playground equipment, and road cones. This method allows for design flexibility and low material waste.












 Fiberglass Fabricators
Fiberglass Fabricators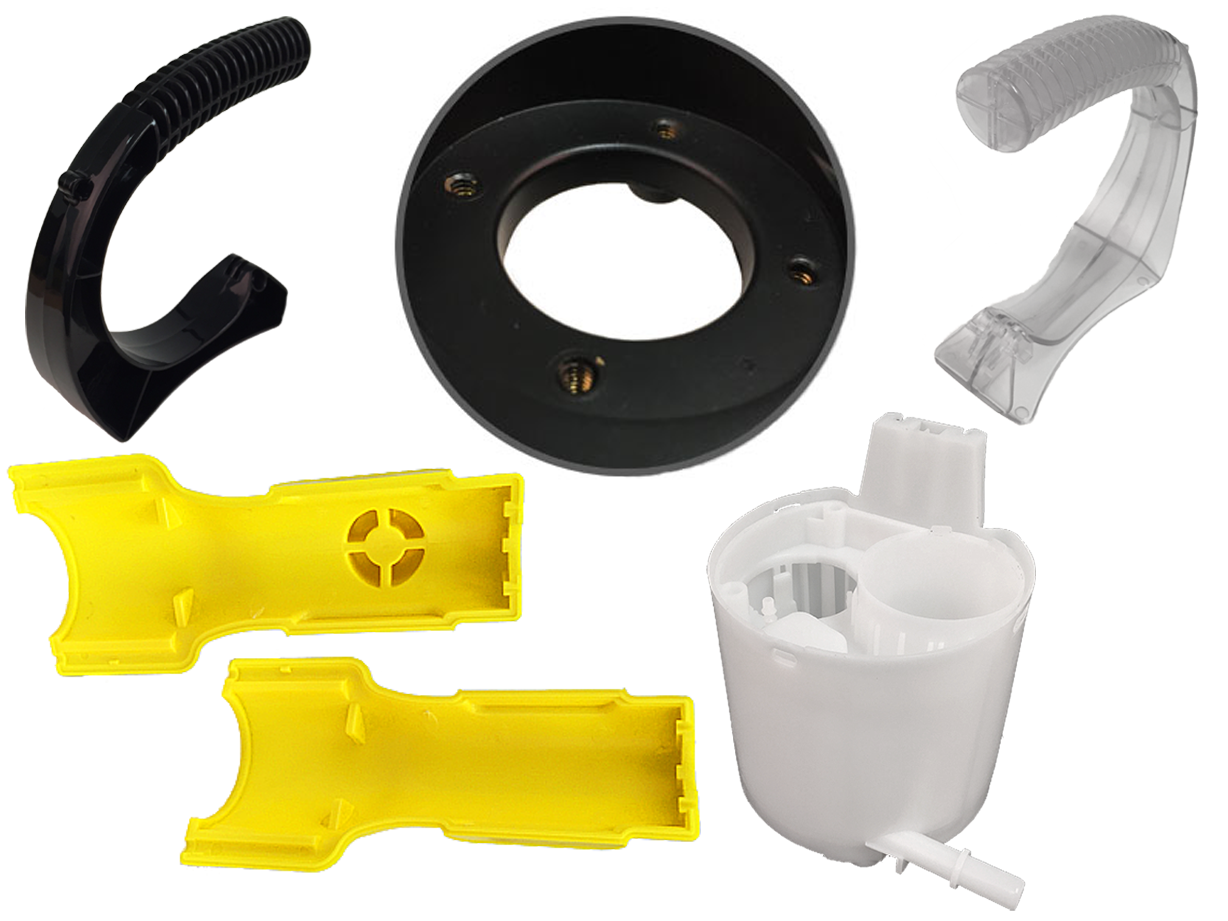 Injection Molded Plastics
Injection Molded Plastics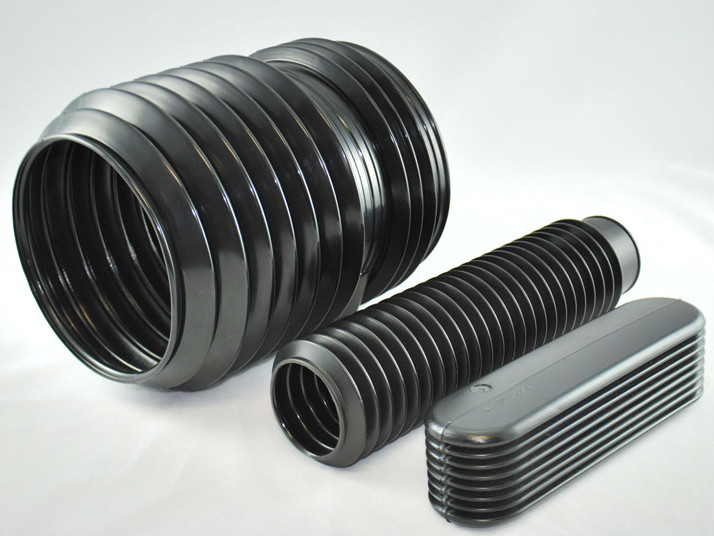 Plastic Blow Molding
Plastic Blow Molding Plastic Dip Molding
Plastic Dip Molding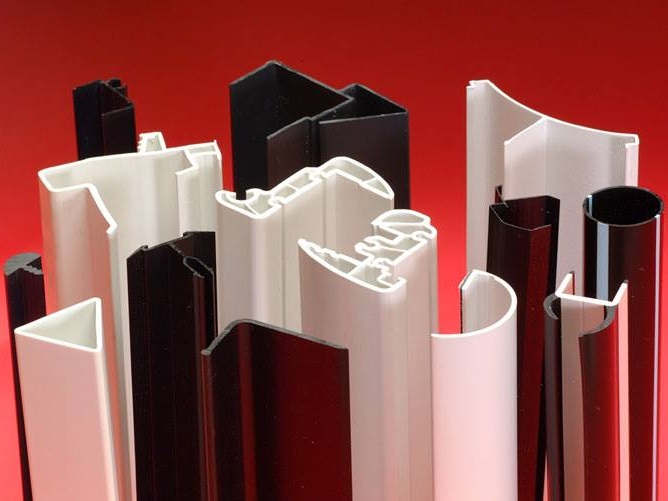 Plastic Extrusions
Plastic Extrusions Plastic Tubing
Plastic Tubing Polyurethane Molding
Polyurethane Molding Rotationally Molded Plastics
Rotationally Molded Plastics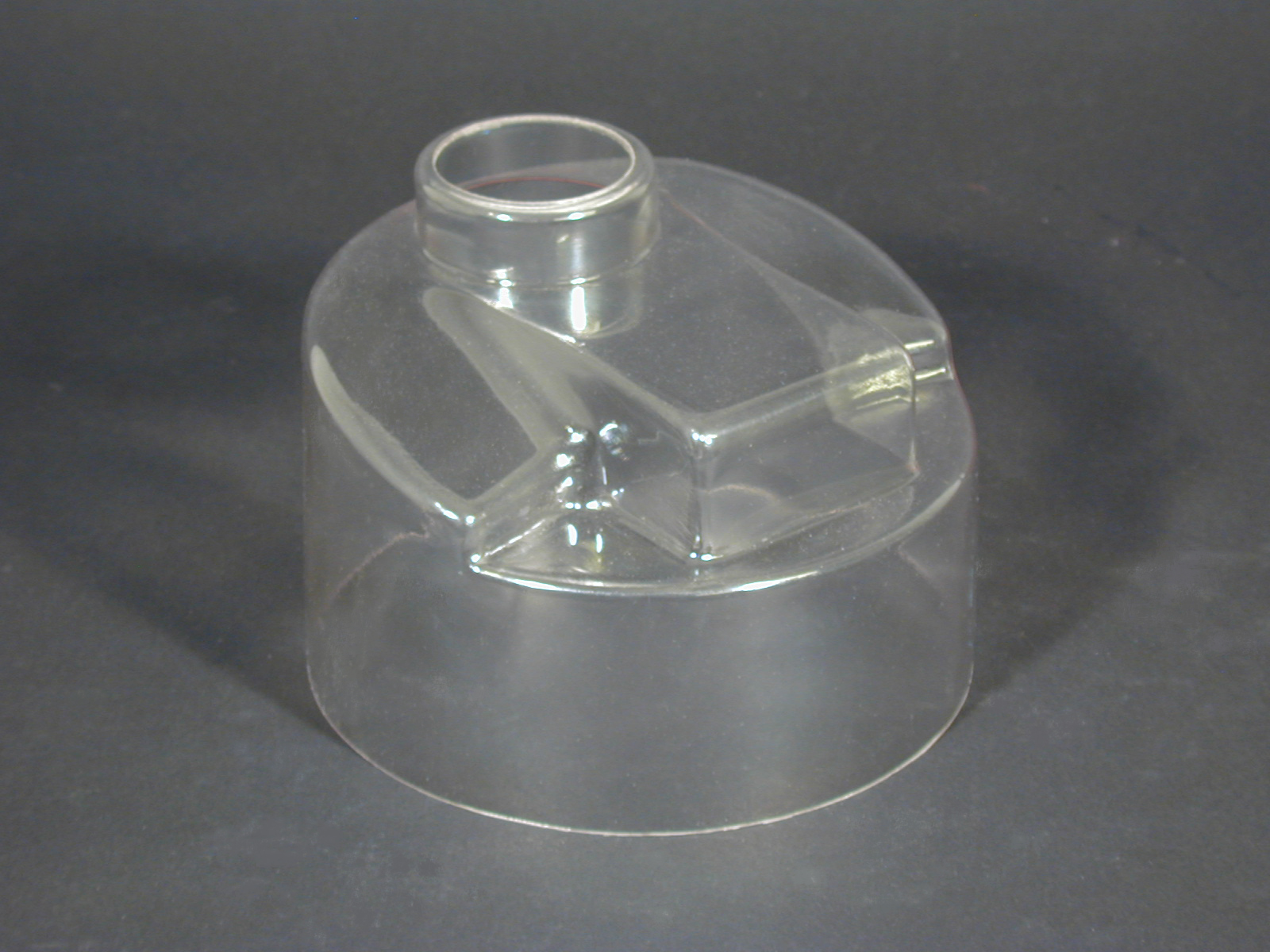 Vacuum Formed Plastics
Vacuum Formed Plastics Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services